The RFID technology is a booming business that helps companies eliminate the manual processes associated with locating and scanning barcodes, cutting costs and errors from manufacturing, transportation, distribution, and retailing operations. For this reason, finding the right combination of RFID hardware (readers, tags, antenna) with software, and printers are important for current and future business operations.
RFID Printers
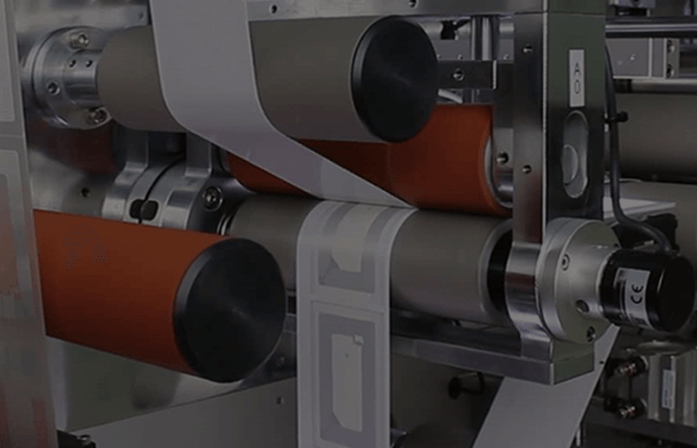
RFID printers are used to print and encode RFID hangtags and smart labels. These printers use a media with an RFID inlay (chip and antenna combination) and are embedded within the label materials. They add specific digital functionality to images by embedding RFID labels into different types of print formats. Conventional RFID printers use an RFID head to print, using thermal transfer technology.
By radio frequency transmission, an RFID encoder that is inside the printer writes data to the tag. The transmission is focused on the specific location of the tag within the label; text, barcodes, and graphics are printed as usual. The encoder/printer performs two tag quality checks; the first one is done prior to encoding to ensure that the inlay is functional and can receive data, while the second one is done to verify that the data was written and stored on the chip correctly.
Thermal transfer printing technology
This printing technology is resistant to environmental elements and has a longer lifespan, therefore, it is commonly used in RFID label and tag printing. A thermal transfer ribbon is required because the printing process involves heating the printhead and pressing it to the back of the thermal ribbon. To create the printed image or text on the RFID, the heated printhead melts the ribbon and transfers the color to the front of the label. The advantages of thermal transfer printing are; little reactance to heat, abrasions, light, and long ink lifespan. The ribbon in between the printhead and label acts as a buffer for foreign items like dirt and dust. The ribbon expands the lifespan of the printhead as well as keeps impurities out of the printed image or text.
The ribbon available for printing on RFID labels and tags includes; wax ribbon, resin ribbon, and wax-resin ribbon. The three differ in image quality, durability, and print lifespan. RFID labels and wet inlays can be run through an RFID printer for printing and encoding purposes. Tags are manufactured on a single longliner, back-to-back therefore, manufacturers have created a way for RFID printers to determine where one tag begins and the other ends. However, depending on the manufacturer and tag type, these separation indicators vary. The most common separation indicators are notch, continuous, and black-mark. Therefore, before an RFID printer starts printing/encoding, it must know the specific separation indicator to know when to print/encode.
Conclusion
RFID printers are getting more enhanced to maximize efficiency and prevent errors, especially now that the utilization of RFID technology intensifies. When purchasing a printer, it is important to know the specifications relating to roll size and media size as well as tags for that printer. The media size width, thickness, and length vary on each printer.
Click here to know what product you can use for your project. If you are not sure, welcome to contact our sales expert any time.
.png)